Breast Milk Storage Guidelines
You’ve gone to the trouble of pumping breast milk so don’t waste that liquid gold. Learn more about breast milk storage to ensure you’re serving up safe pumped breast milk.
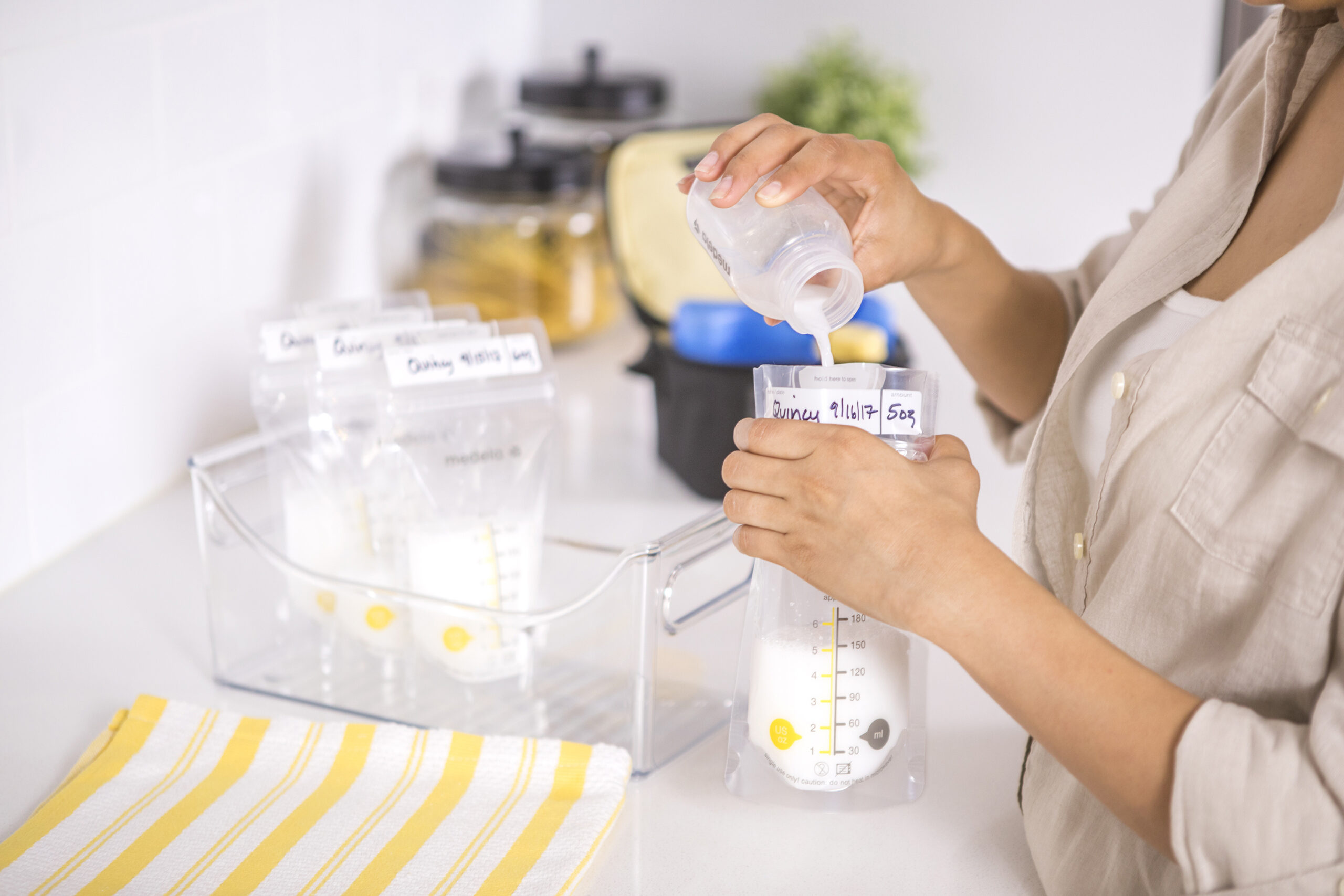


Welcome, new moms and seasoned pros alike, to a topic that’s as precious as it is practical: storing pumped breast milk. If you’re a breastfeeding mom, you already know the incredible benefits of breast milk for your baby’s health and development. And if you’re navigating the world of breast pumping, you’re likely finding that your “liquid gold” can sometimes feel more like a science experiment.
Fear not! We’re here to simplify the process and help you make sure that every precious drop of your breast milk is safely stored and ready to nourish your little one whenever they need it. Whether you’re pumping to build a freezer stash, preparing for a return to work, or just looking for some handy storage tips, we’ve got you covered.
Using stored breast milk might seem like a straightforward task, but there are some guidelines that can make the process clearer. Whether you’re planning a night out, heading back to work, or just want to let someone else share in the joy of feeding your little one, we’ve got your back.
Breast Milk Storage Guidelines
Freshly pumped milk
Room temperature: up to 4 hours
Refrigerator: up to 4 days
Freezer: 6-12 months
Thawed, previously frozen
Room temperature: up to 2 hours
Refrigerator: up to 24 hours
Freezer: never refreeze breast milk after it’s been thawed
Left over from a feeding (meaning your baby did not finish bottle)
Room temperature: use within 2 hours after baby has finished eating
Refrigerator: use within 2 hours after baby has finished eating
Freezer: do not freeze
Have more questions? Listen to our FREE podcast!
LISTEN NOWReady to use that breast milk? Take note of these general guidelines to ensure that your baby’s milk is served up properly!
Thawing frozen breast milk for immediate use
Warm the milk by running warm water over the bag or bottle and use it within the next 24 hours.
Warming refrigerated breast milk
Warm the milk by running warm water over the bag or bottle until it’s at room temperature.
Note: Never thaw or heat breast milk in the microwave.
Buy Milk Storage Bags Online

The information contained here within is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor, go to the emergency department, or call 911 immediately. Edwards Health Care Services (EHCS) does not recommend or endorse any specific tests, physicians, products, procedures, opinions, or other information that may be mentioned here within. Reliance on any information provided by EHCS, EHCS employees, contracted writers, or medical professionals presenting content for publication here within is solely at your own risk.
Sources:
• Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Proper Storage and Preparation of Breast Milk
Tags: Baby, Breastfeeding, Breastmilk, Feeding, Guidelines, Pumping, Storage