Hyperglycemia vs. Hypoglycemia
Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) can be a sign of diabetes onset, and it usually continues to occur on and off after you start treatment. On the other hand, hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) occurs as the result of diabetes treatment, particularly related to insulin. It is important to know the symptoms for early treatment.

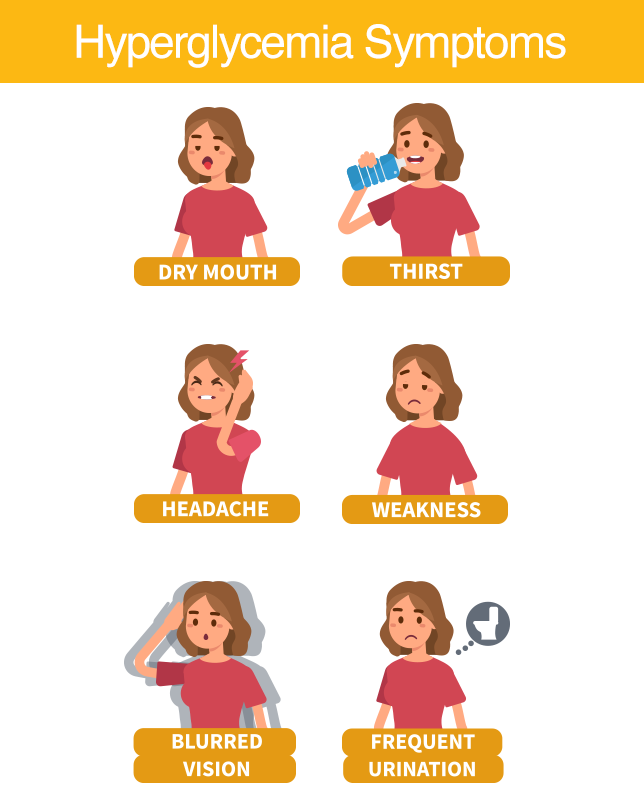
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Glucose)
Hyperglycemia is when the body can’t use insulin properly or has too little insulin. This causes blood glucose to go above target range or higher than 160 mg/dL. It is important to know the symptoms and treatment options.
Treating Hyperglycemia
-
Be sure to drink plenty of water. It is recommended that you drink at least 8 glasses per day.
-
Ask yourself what may have caused high blood glucose/low blood glucose, and take action to correct it.
-
Try to determine if there is a pattern by checking your blood glucose.
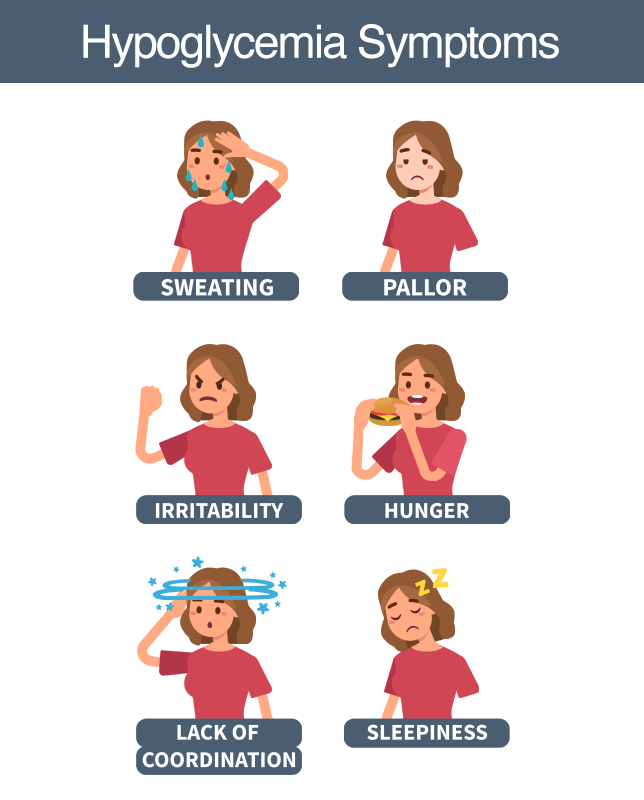
Hypoclycemia (Low Blood Glucose)
Hypoglycemia is when your blood glucose level is less than 70 mg/dL or your blood glucose level goes below your individual target range.
Treating Hypoglycemia
Always consult with your doctor or diabetes educator to review your testing results if you are not sure what to do.
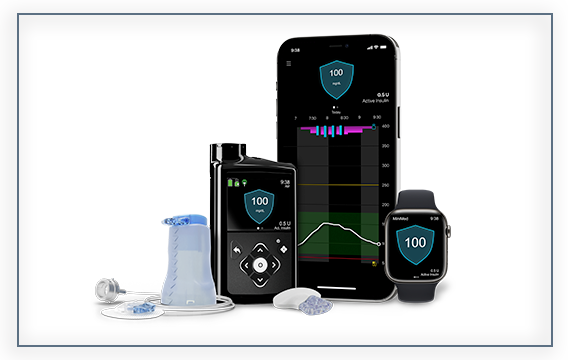
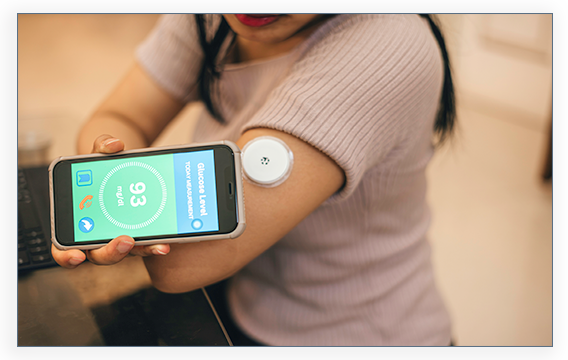
Do you need a CGM?
Apply Today!Tags: Diabetes, Diabetes Complications, Diabetes Management